Kubernetes Templates
Browse our collection of pre-built Kubernetes templates to quickly deploy your applications.
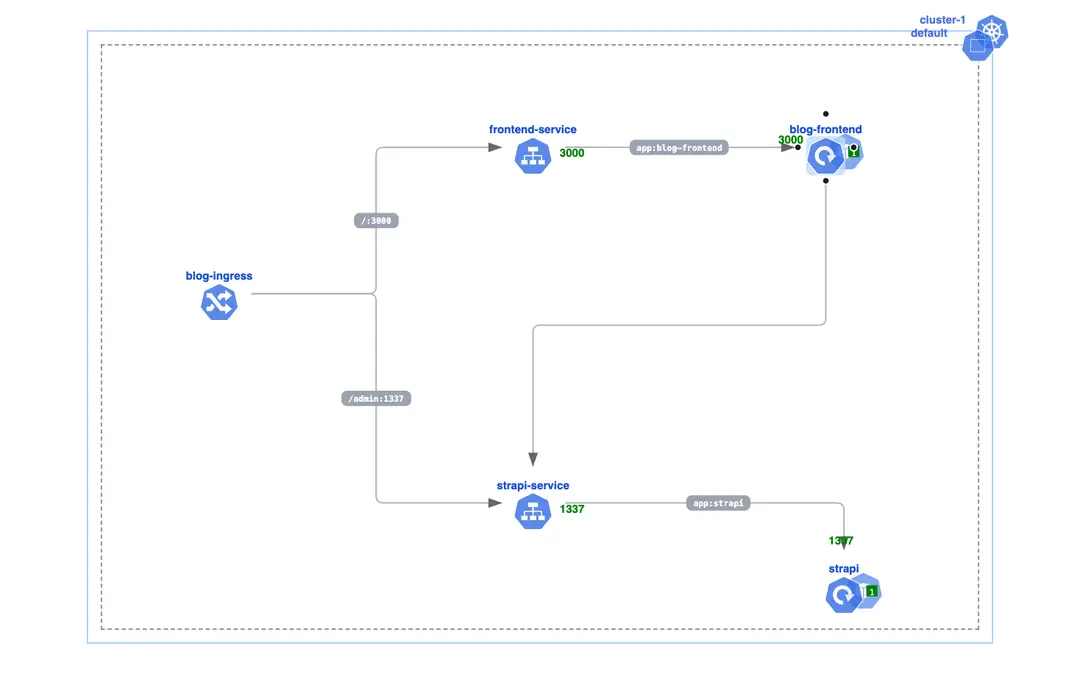
Headless CMS - Strapi-Next.js Kubernetes Template
233 usesThis ready-to-deploy Kubernetes template provides a complete full-stack blog platform combining Strapi CMS backend with Next.js frontend, ready for immediate Strapi deployment for a headless CMS.
## What This Template Creates for Your Kubernetes Deployment
This Strapi self-hosted template simplifies your setup, removing the need for complex manual configuration.
### Backend Infrastructure:
- **Strapi CMS (port 1337)** - A Headless CMS for blog content creation and API endpoints. The port is pre-configured, so you don't need to manually change strapi port.
- **ClusterIP service** for internal backend connectivity.
### Frontend Application:
- **Next.js Blog Frontend (port 3000)** - Modern React-based blog interface for content display.
- **ClusterIP service** for internal frontend connectivity.
### Smart Routing:
**Ingress Controller with path-based routing:**
- `/admin` Strapi admin interface for content management and
- `/` Next.js frontend for public blog access.
This configuration automates a typical Kubernetes NextJS setup.
## Key Features for Strapi & Next.js Deployment
**Production-Ready:** Complete application stack with proper service isolation.
**Development-Friendly:** Uses local Docker images with imagePullPolicy: Never.
**Scalable Architecture:** Kubernetes deployments enable easy horizontal scaling.
**Smart Routing:** Single entry point with intelligent path-based traffic distribution.
**Modern Stack:** Combines headless CMS flexibility with React performance.
## Perfect For
- Content Creators wanting a modern, manageable blog platform.
- Developers learning full-stack Kubernetes deployments.
- Teams needing separation between content management and presentation.
- Projects requiring scalable, cloud-native blog infrastructure.
## Prerequisites & Deployment
- Kubernetes cluster (Docker Desktop/Minikube)
- NGINX Ingress Controlle
strapikubernetesCMS+1 more
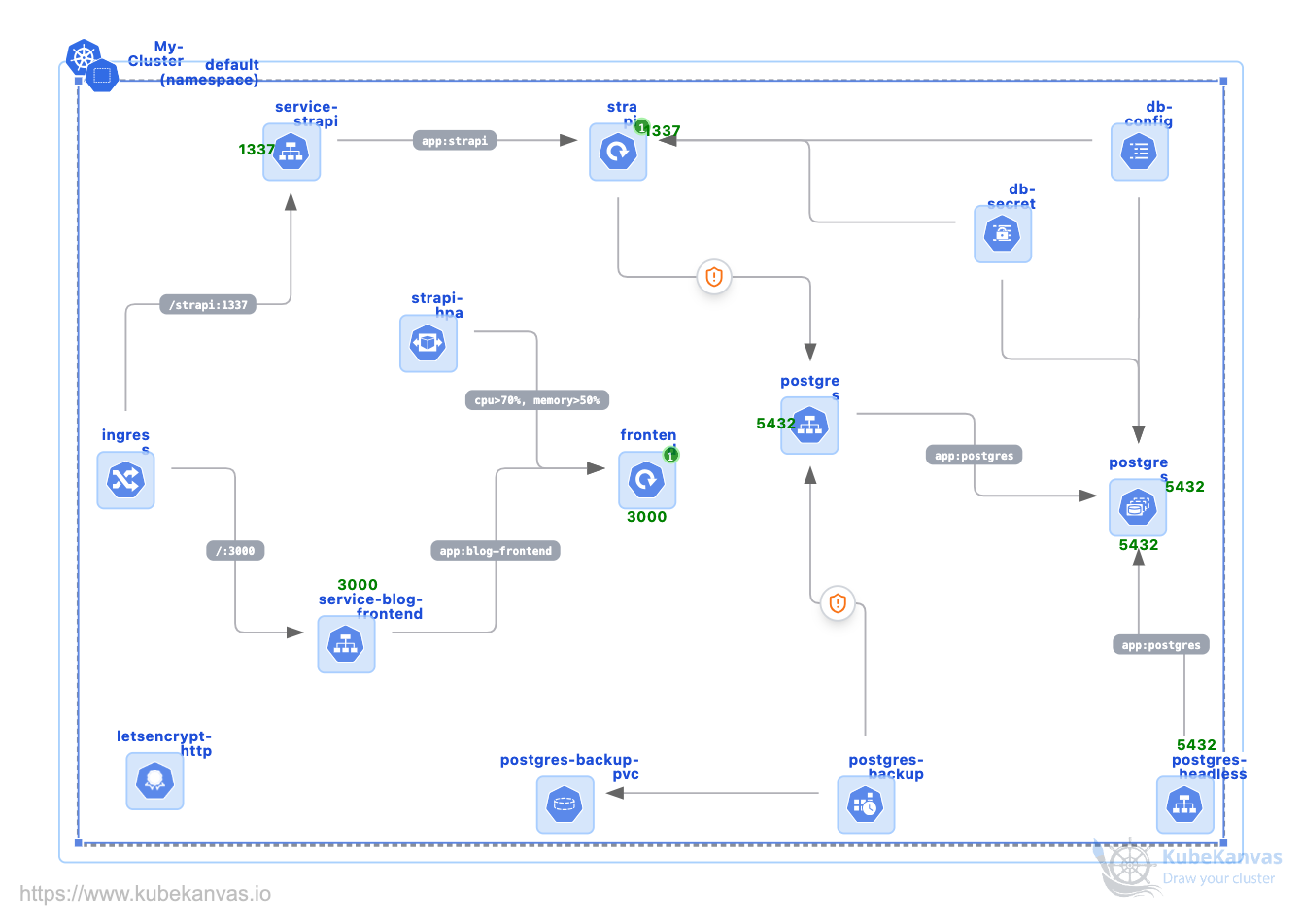
Deploying Your Production Blog - Next.js, Strapi, Database and ConfigMaps
198 uses
This template covers essential Kubernetes YAML manifests for a production-ready Strapi + Next.js blog platform. It's the ultimate guide for a production Kubernetes setup.
## Key Components for Your Next.js Kubernetes Deployment
- **PostgreSQL StatefulSet:** Provides a stable Kubernetes database with 10Gi persistent storage, health probes, and resource limits (256Mi-512Mi memory).
- **Services:** Headless service for StatefulSet identity management + ClusterIP for application access.
- **Configuration:** A Kubernetes ConfigMap stores non-sensitive data (host, port), and a Secret manages credentials securely with base64 encoding.
- **Storage:** Volume claim templates for the PostgreSQL database, a 10Gi PVC for media uploads, and 20Gi for backups.
- **Security:** Let's Encrypt ClusterIssuer automates TLS certificates, while Ingress handles HTTPS termination and routing for a secure Strapi deployment.
- **Scaling:** HPA auto-scales based on CPU (70%) and memory (80%) utilization with proper resource requests/limits.
- **Backups:** A CronJob performs daily PostgreSQL backups at 2 AM with 7-day retention and gzip compression.
strapipostgresqlhorizontalpodscaling
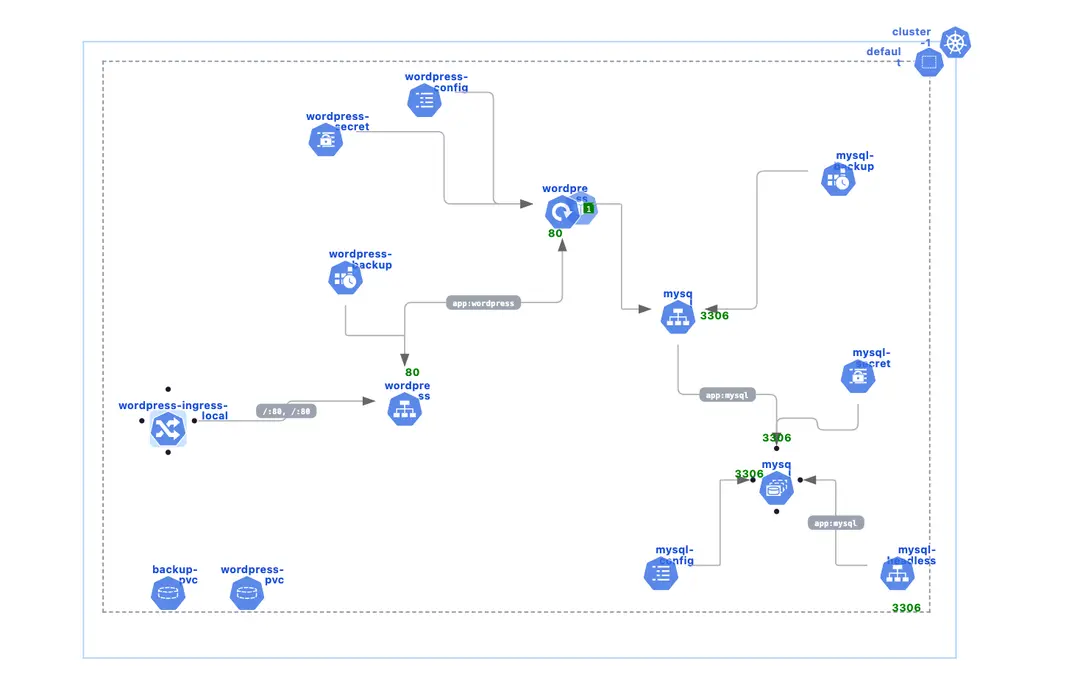
High-Availability WordPress Template for Deployment on Kubernetes
128 usesDeploy a production-ready, scalable WordPress platform on Kubernetes with this comprehensive template. This single YAML file contains all the necessary manifests to run a high-availability WordPress setup with MySQL database, auto-scaling, SSL termination, and automated backups
## What's Included:
**Core Infrastructure:**
- **MySQL StatefulSet** with persistent storage and health checks
- **WordPress Deployment** with 3 replicas for high availability
- **ConfigMaps and Secrets** for secure configuration management
-**Services** for internal communication and load balancing
**Production Features:**
- **SSL/TLS termination** with Let's Encrypt certificate management
- **Ingress controller** integration for external access
- **Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA)** for automatic scaling based on CPU/memory
- **Resource limits and requests** for optimal resource allocation
- **Health checks** and readiness probes for reliable deployments
**Data Management:**
- **Persistent Volume Claims** for database and WordPress file storage
- **Automated backup CronJobs** for both MySQL database and WordPress files
- **Data retention policies** to manage backup storage efficiently
**Security & Performance:**
- **Security contexts** with proper user permissions
- **Rate limiting** and proxy configurations via Ingress annotations
- **Session affinity** for consistent user experience
- **Resource optimization** with memory and CPU tuning
## PrerequisitesBefore deploying this template, ensure your Kubernetes cluster has:
- **cert-manager** installed for SSL certificate management
- **Ingress controller** (NGINX recommended) running
- **Storage class** configured for dynamic volume provisioning- At least **3 worker nodes** for high availability
## Quick Start
1. **Customize the template**: Replace placeholder values like `your-wordpress.com` and `[email protected]`
2. **Generate WordPress auth keys**: Visit http
WordpressMySQLHigh available
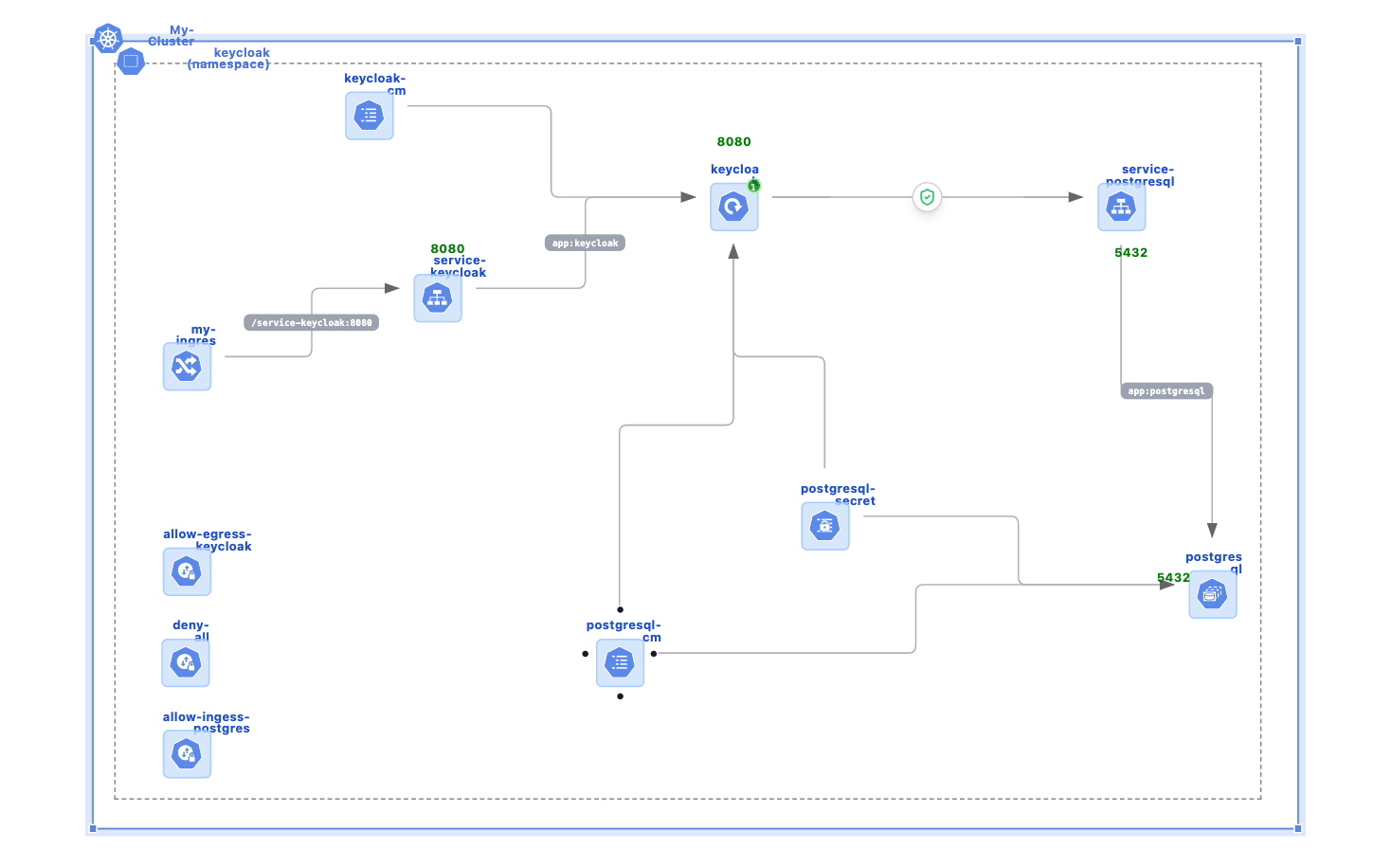
Keycloak with postgresql database
34 usesBasic keycloak deployment in kubernetes with following components
1) Keycloak
2) Keycloak image configuration in configmap
3) Postgresql database as statefulset with PVC template
4) Network policies to only allow connections between keycloak and databse
5) Ingress to reach the keycloak
keycloak
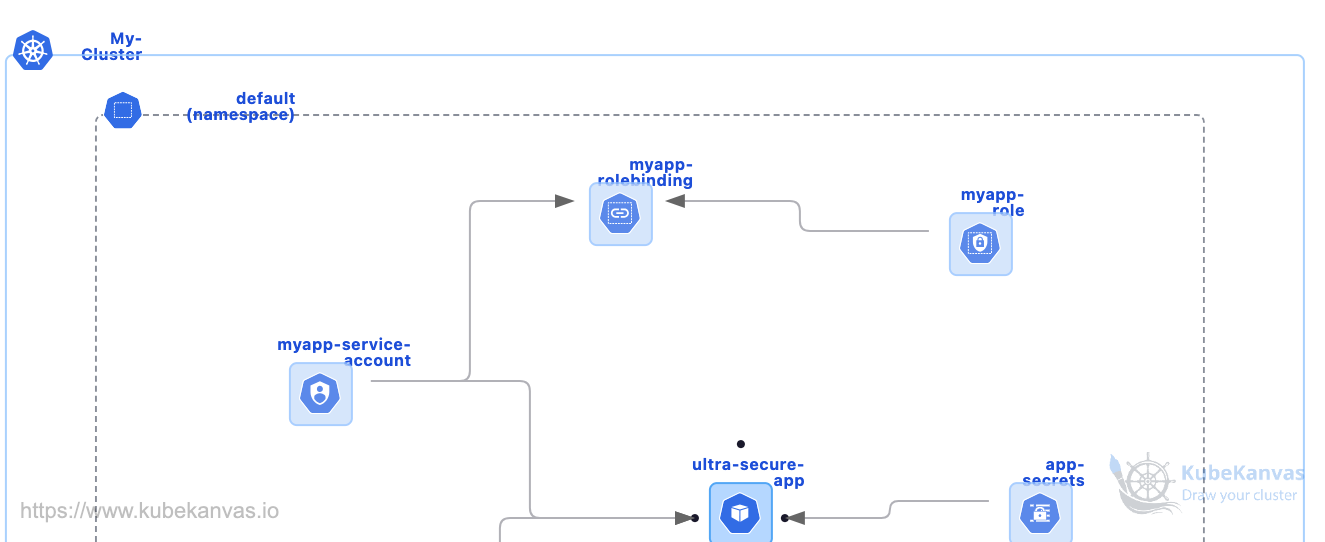
Ultra Secure Kubernetes Pod
21 uses# Ultra-Secure Kubernetes Pod Template
> **Related Article**: This code accompanies the tutorial "[Securing Kubernetes Pods: A Complete Guide to Pod-Level Security Configuration](https://www.kubekanvas.io/blog/securing-kubernetes-pods-a-complete-guide-to-pod-level-security-configuration)" published on KubeKanvas.io.
The article provides a comprehensive guide to deploying a modern headless CMS using Strapi on Kubernetes, covering everything from containerization to production-ready deployments with persistent storage, ingress routing, and scalability considerations.
## What This Template Provides
A production-ready, security-hardened Kubernetes pod configuration implementing industry best practices to protect your workloads from common attack vectors.
## Security Features Included
### Identity & Access Control
- Dedicated service account with minimal RBAC permissions
- API token mounting disabled to prevent credential exposure
### Process Security
- Non-root user execution (UID 1000)
- Privilege escalation prevention
- All Linux capabilities dropped, only `NET_BIND_SERVICE` added
- Read-only root filesystem with temporary volumes
### Linux Security Modules
- Seccomp runtime default profile
- AppArmor enforcement
- SELinux multi-level security labels
### Image Security
- Pinned image version (no `latest` tags)
- Private registry integration
- Always pull policy for latest security patches
### Resource Protection
- CPU, memory, and ephemeral storage limits
- Prevents resource exhaustion attacks
### Secret Management
- Kubernetes Secrets for sensitive data
- Environment variables from SecretRefs
- Volume-mounted secrets with restricted permissions (0400)
### Health Monitoring
- Liveness and readiness probes configured
## Quick Start
Copy this template and customize the image, secrets, and resource limits for your application. All security controls are pre-configured following the principle of least privilege.
Pod SecuritySecurity through manifest
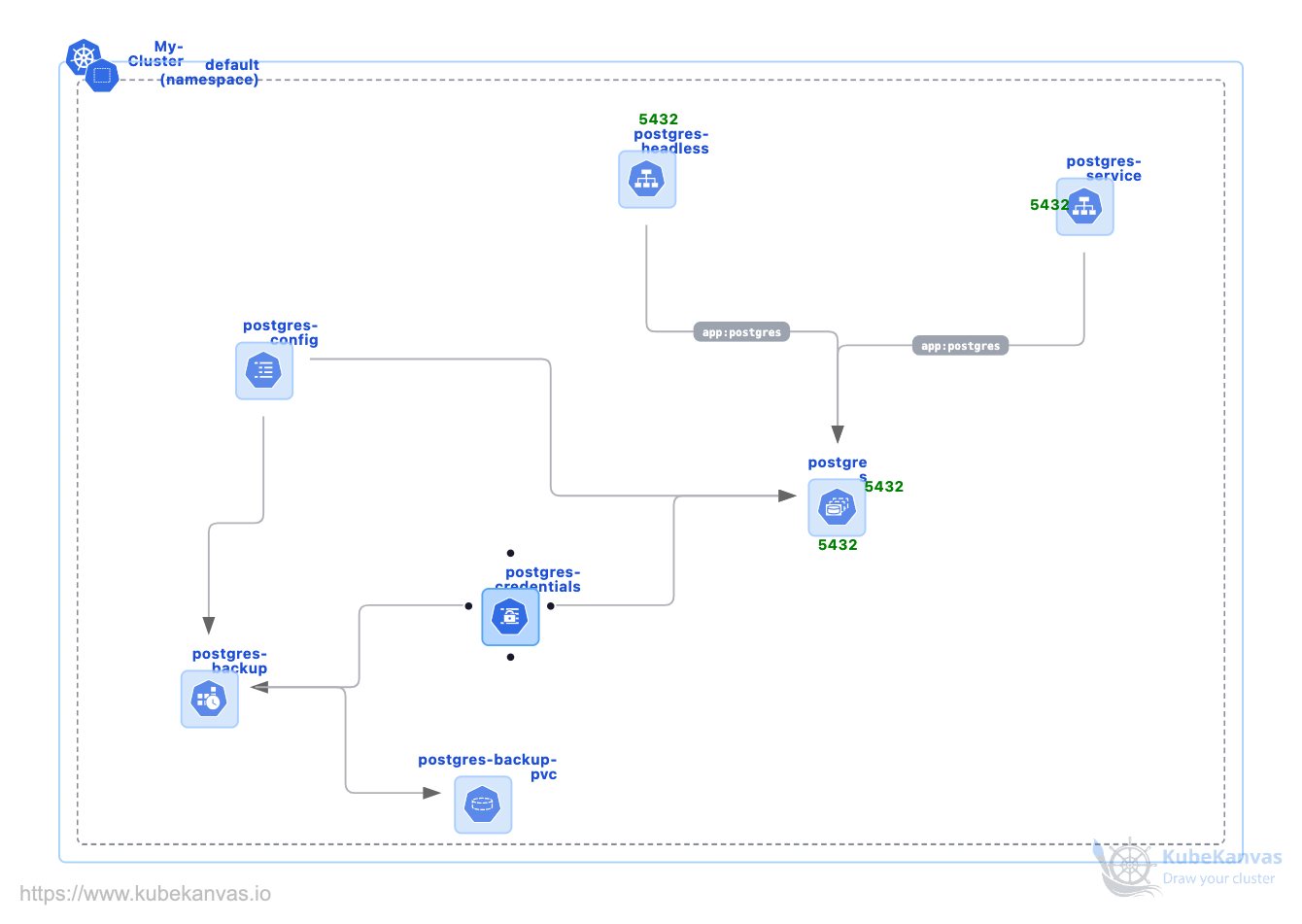
Deploy Postgresql in Kubernetes with backup
0 usesThis Kubernetes template deploys a **stable, persistent, and production-grade PostgreSQL database** using StatefulSets, Headless Services, and Persistent Volumesdesigned specifically for cloud-native and Kubernetes-first environments. It eliminates common database pitfalls in Kubernetes such as **data loss, unstable networking, and insecure configuration**.
---
## What This Template Creates for Your Kubernetes Cluster
This PostgreSQL StatefulSet template provides a clean, modular database deployment without fragile workarounds.
### Database Infrastructure
- **PostgreSQL 15 (Alpine)** Lightweight, production-ready relational database
- **StatefulSet** Guarantees stable Pod identity (`postgres-0`) and ordered lifecycle
- **Persistent Volume Claim (PVC)** Ensures data survives Pod restarts and rescheduling
- **ReadWriteOnce storage** Safe disk attachment for database workloads
### Networking & Access
- **Headless Service (`clusterIP: None`)**
- Enables direct Pod DNS resolution
- Required for backups, replication, and database-aware clients
- Resolves to stable Pod names like:
```text
postgres-0.postgres-headless
```
### Configuration & Security
- **ConfigMap**
- Database name
- Database user
- **Kubernetes Secret**
- Database password (not hardcoded)
- **Environment-based injection**
- Clean separation between code and credentials
### Health & Stability
- **Readiness Probe (`pg_isready`)**
- Ensures traffic is only sent when PostgreSQL is fully ready
- **Sticky storage**
- Data automatically reattaches even after Pod recreation
---
## Key Features of This PostgreSQL Kubernetes Deployment
**Production-Ready** Built using Kubernetes best practices for stateful workloads
**Persistent Data Safety** Data is never lost when Pods restart or move between nodes
**Predictable Networking** Stable DNS and Pod identity via Headless Service
PostgresqlStatefulsetPostgresql with backup
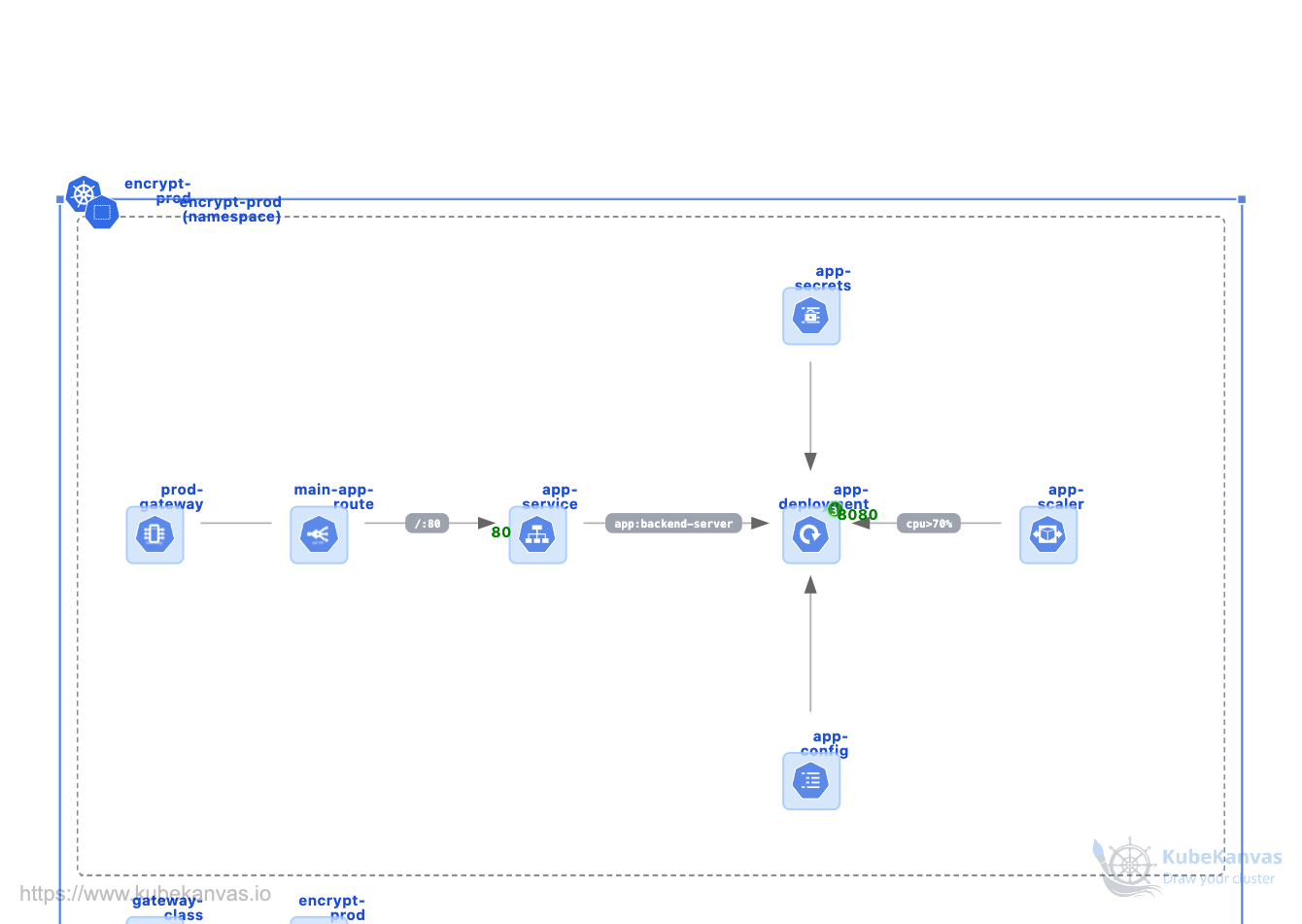
Gateway API Application Stack with Kubernetes
1 use# Kubernetes Gateway API Template
This Kubernetes template deploys a **scalable, secure, and modern application architecture** utilizing the **Gateway API**the next-generation standard for service networking.
Designed for organizations moving beyond the limitations of standard Ingress, this manifest provides a modular, role-oriented framework that separates infrastructure management from application development.
It eliminates common networking pitfalls such as **annotation sprawl**, manual SSL management, and rigid traffic routing.
---
## What This Template Creates for Your Kubernetes Cluster
This stack provides a complete "browser-to-pod" flow, integrating advanced traffic management with automated security and scaling.
### 1. Next-Gen Traffic Infrastructure
- **GatewayClass** Defines the infrastructure provider (e.g., Envoy or Istio) and establishes the organizational standard for load balancing
- **Gateway (prod-gateway)** Acts as the entry point for all external traffic, managing public IP addresses and entry ports (HTTPS/443)
- **HTTPRoute (main-app-route)** Provides sophisticated L7 routing logic, mapping hostnames and URL paths to internal services
### 2. Automated Security & Identity
- **Cert-Manager Integration** Automatically provisions and renews SSL/TLS certificates via Let's Encrypt using the `ClusterIssuer`
- **app-tls-secret** A dynamically managed secret created by Cert-Manager to secure the "Front Door" with high-grade encryption
- **app-secrets** A secure, opaque storage for sensitive application data like database passwords and API keys, keeping them out of your source code
### 3. Decoupled Configuration & Discovery
- **ConfigMap (app-config)** Centralizes non-sensitive environment variables (log levels, API URLs), allowing configuration changes without rebuilding container images
- **Headless-Ready Service** Bridges the gap between the Gateway and the backend, providing stable DNS names for routing
#Kubernetes#GatewayAPI#CloudNative+3 more
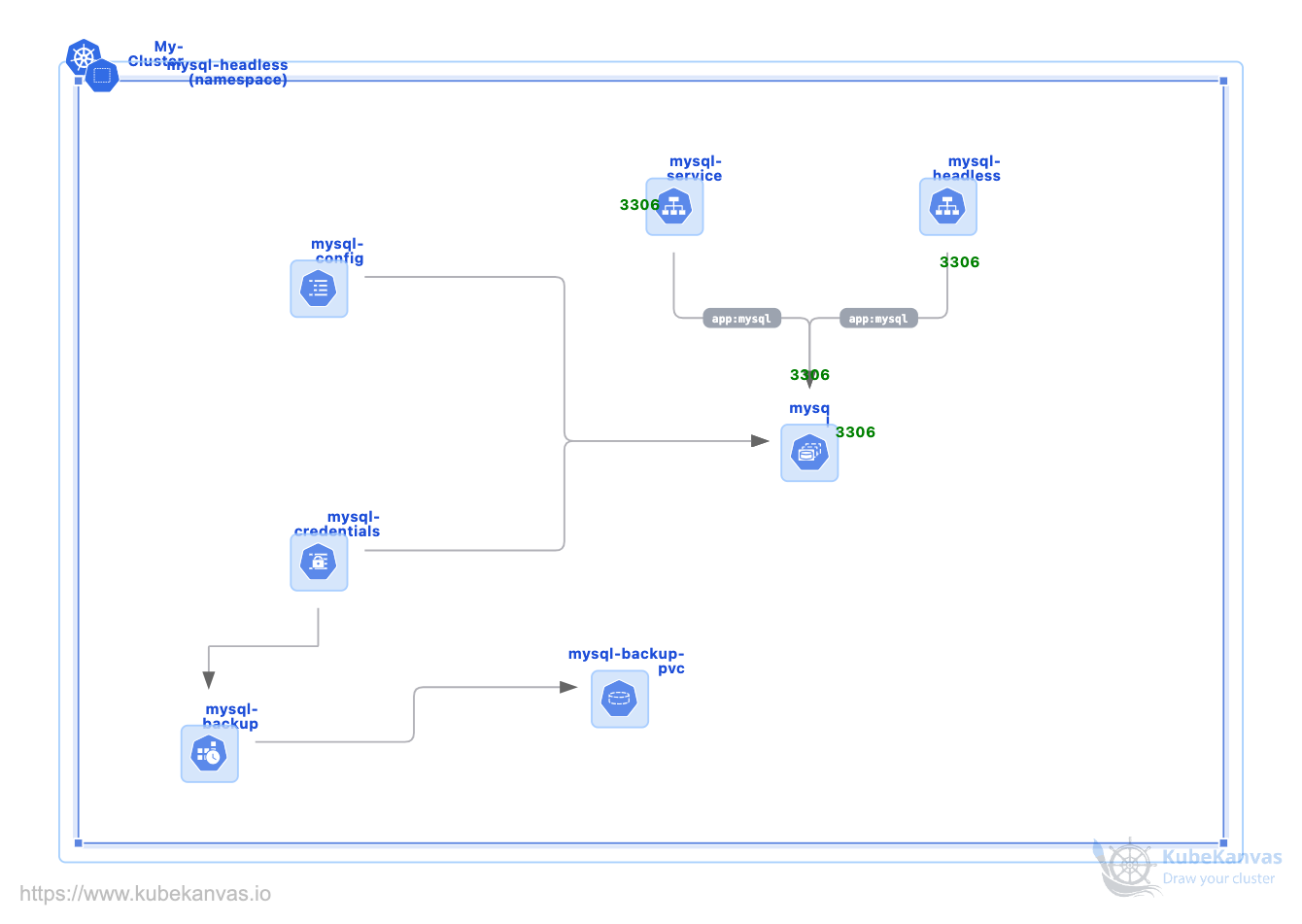
Deploy MySQL in Kubernetes with backup
0 uses
This Kubernetes template deploys a **stable, persistent, and production-grade MySQL database** using **StatefulSets**, **Headless Services**, and **Persistent Volumes**. It is architected to handle the specific challenges of running stateful database workloads in dynamic, containerized environments.
By using this template, you avoid the risks of data loss and networking instability common in standard **Deployment** objects, ensuring your MySQL instance remains reliable under production pressure.
---
### What This Template Creates for Your Cluster
This MySQL configuration provides a modular, **best-practice** infrastructure for your data layer.
---
### **Database Infrastructure**
* **MySQL 8.0** A high-performance, industry-standard relational database.
* **StatefulSet** Unlike a Deployment, this guarantees stable Pod names (e.g., `mysql-0`, `mysql-1`) and ordered startup and termination.
* **VolumeClaimTemplates** Automatically provisions a dedicated Persistent Volume (PV) for each replica, ensuring data remains mapped to the correct Pod identity.
---
### **Networking & Access**
* **Headless Service (`ClusterIP: None`)** Essential for discovery; it allows applications or backup scripts to address individual Pods directly.
* Provides stable DNS endpoints such as:
`mysql-0.mysql-headless.default.svc.cluster.local`
* **Standard Service** Provides a single, load-balanced IP for applications to connect to the active database endpoint.
---
### **Configuration & Security**
* **ConfigMap** Centralizes non-sensitive settings such as the default database name (`MYSQL_DATABASE`).
* **Kubernetes Secrets** Securely manages the root password and application user credentials, preventing sensitive data from being committed to version control.
* **SecurityContext** Enforces non-root execution (UID `1001`) and sets filesystem permissions (`fsGroup`) to ensure MySQL can safely read and write persistent data.
#MySQL#StatefulSet#CronJob+1 more
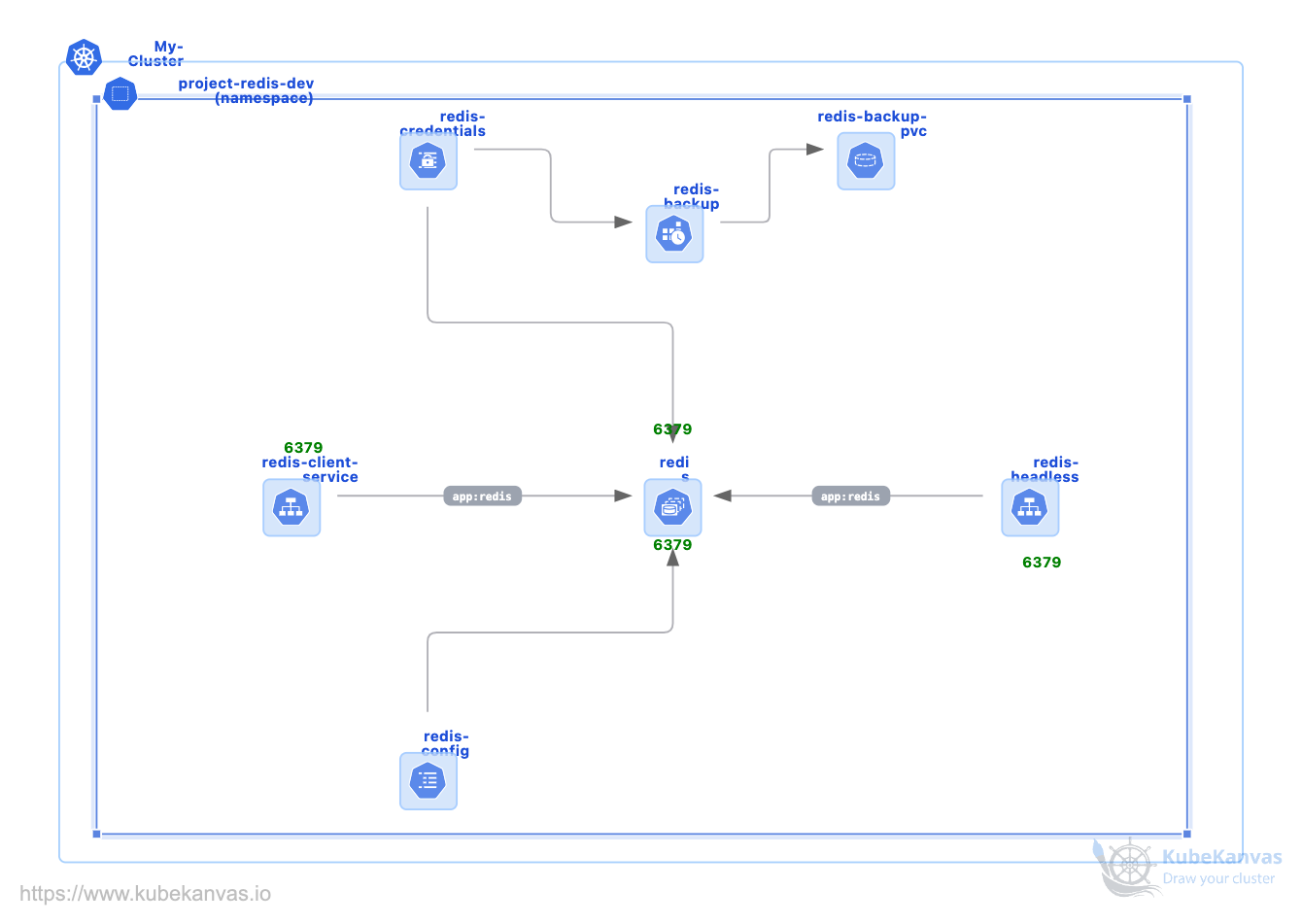
Kubernetes Redis Deployment: Client Service Access and Verification
14 uses---
# **Redis via Client Service Using a Temporary Pod**
**Namespace:** `project-redis-dev`
**Redis Pods:** `redis-0`, `redis-1`, `redis-2`
**Client Service:** `redis-client-service`
**Password:** `mypassword`
---
## **Step 1: Launch Temporary Client Pod**
```bash
kubectl run redis-client-test --rm -it --image=redis:7-alpine --restart=Never --namespace default -- sh
```
* `--rm` deletes pod on exit
* `-it` interactive shell
* `-- sh` shell in Alpine image
---
## **Step 2: Connect via Client Service**
Inside pod shell:
```bash
redis-cli -h redis-client-service -p 6379 -a mypassword
```
* Connects through **ClusterIP service** (load-balanced across pods)
---
## **Step 3: Test Redis Commands**
```text
PING
SET testkey "Hello via client service"
GET testkey
```
**Expected Output:**
```
PONG
OK
"Hello via client service"
```
* `PING` connectivity check
* `SET` write data
* `GET` read data
> `testkey` is just a sample key; replace as needed.
---
## **Step 4: Exit**
```text
QUIT
```
Then exit pod shell (`Ctrl+D`). Pod auto-deletes.
---
**Result:**
* Redis is reachable **via client service**
* **Read/write operations** verified
* No local Redis installation needed
---
RedisStatefulSetKubernetes+2 more
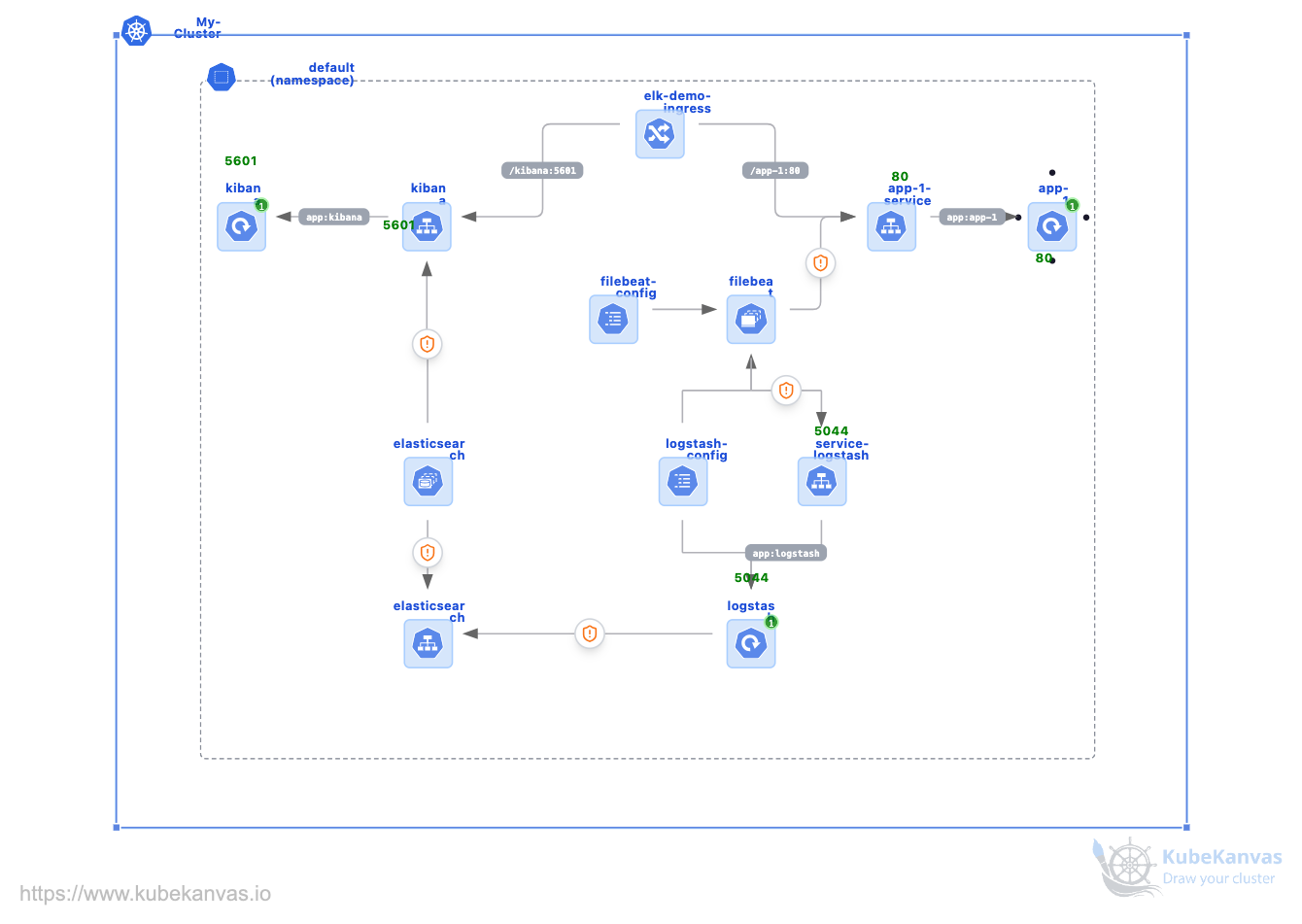
ELK Stack on Kubernetes: Collect, Store, and Visualize Nginx Logs
3 uses
# Monitoring Application Logs with ELK on Kubernetes (Nginx)
Monitoring logs is crucial for any app. This setup uses **Nginx** as a sample app, **Filebeat** to collect logs, **Logstash** to process them, **Elasticsearch** to store, and **Kibana** to visualize all on Docker Desktop Kubernetes.
---
## Accessing App and Kibana
* **Ingress:** Access Nginx at `http://elk.local/app-1` and Kibana at `http://elk.local/kibana`.
* **Port-forward:**
```
kubectl port-forward svc/app-1-service 8080:80 -n elk-demo1
kubectl port-forward svc/kibana 5601:5601 -n elk-demo1
```
---
## ELK Components
* **Nginx:** Serves requests, generates logs in `/var/log/nginx`.
```
kubectl get pods -n elk-demo1
kubectl logs <nginx-pod> -n elk-demo1
```
* **Filebeat:** Collects container logs and forwards to Logstash.
```
kubectl logs <filebeat-pod> -n elk-demo1
```
* **Logstash:** Parses and forwards logs to Elasticsearch.
```
kubectl logs deployment/logstash -n elk-demo1
```
* **Elasticsearch:** Stores logs; check indices:
```
curl http://localhost:9200/_cat/indices?v
```
* **Kibana:** Visualizes logs; check pod logs if issues arise:
```
kubectl logs deployment/kibana -n elk-demo1
```
---
## Log Flow
1. Nginx writes logs 2. Filebeat collects 3. Logstash parses 4. Elasticsearch stores 5. Kibana visualizes.
---
## Troubleshooting
* **Port-forward fails:** Ensure pods are `Running`.
* **No logs in Kibana:** Verify indices in Elasticsearch and Filebeat config.
* **Filebeat not sending:** Check file paths and permissions.
---
## Key Commands
```
kubectl get pods -n elk-demo1
kubectl logs <pod> -n elk-demo1
kubectl port-forward svc/<service> <local>:<target> -n elk-demo1
curl http://localhost:9200/_cat/indices?v
```
---
**Summary:** Nginx logs are collected by Filebeat, processed by Logstash, stored in Elasticsearch, and visualized via Kibana. Access via Ingress or port-forwarding. This lightweight stack is ideal for learning ELK
ElasticsearchKubernetesLog Monitoring+3 more
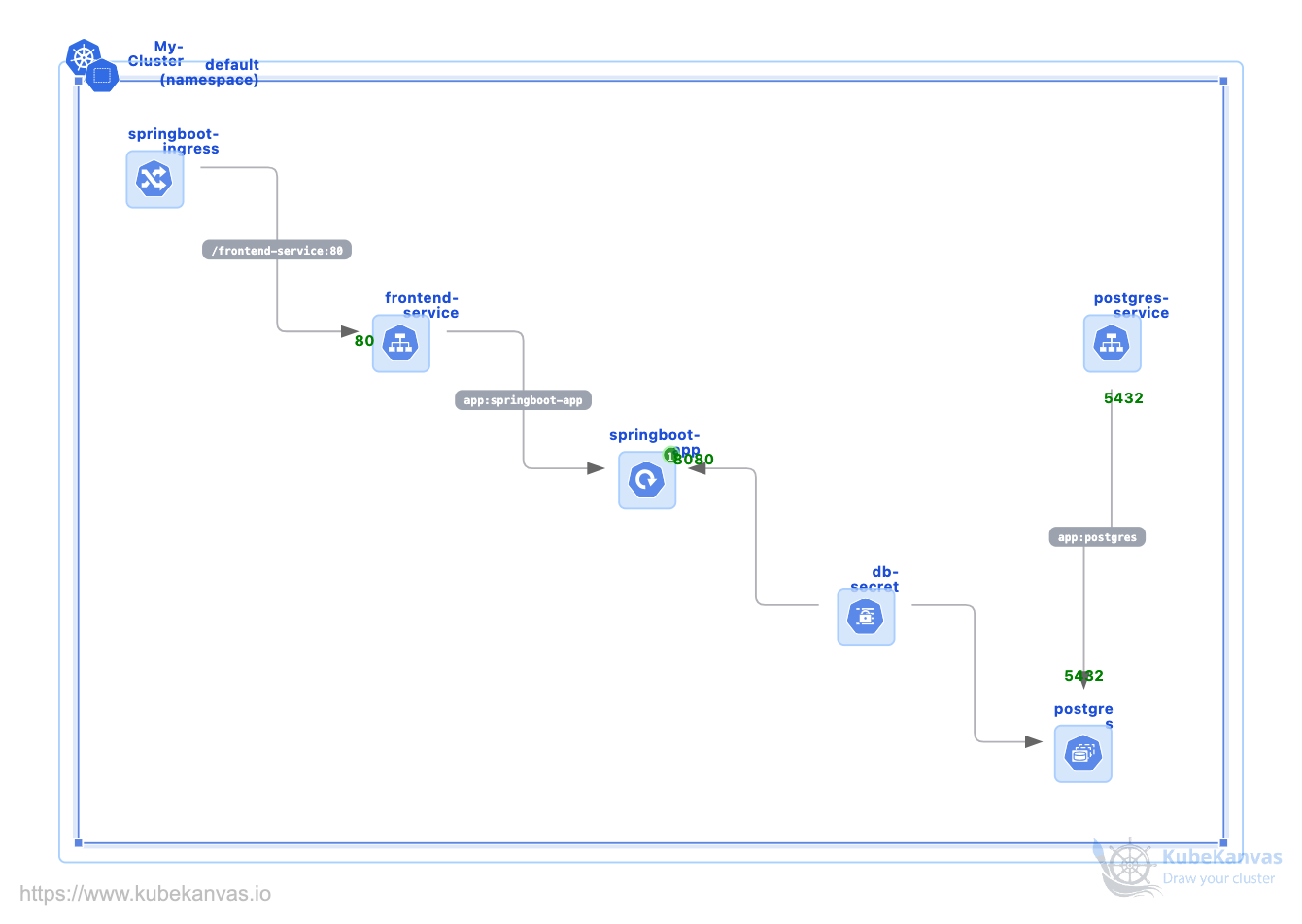
Deploying a Spring Boot App Via Kubekanvas
0 uses# Deploying a SpringBoot Application in Kubernetes with Postgresql and Ingress
In this template, well walk through the deployment of a Spring Boot application with a persistent PostgreSQL database.The deployment was managed via **kubekanvas** (a visual kubernetes IDE) . Here are the "pillars" of our K8s setup:
### 1. The Spring Boot Deployment
The application is "stateless" meaning if a pod dies, Kubernetes can simply spin up a new one without worrying about local data loss.The pod connects to PostgreSQL using a headless service DNS.
The `kubekanvas/springbootstarter:latest` image is pulled from Docker Hub by default, where the Kubernetes container runtime automatically expands it to https://hub.docker.com/r/kubekanvas/springbootstarter.
### 2. The StatefulSet
For databases, standard "Deployments" are risky because pod names and storage can change. By using a **StatefulSet**, we gave our Postgres pod a stable identity (`postgres-0`) and a **Persistent Volume Claim (PVC)**. Even if the pod crashes, the data stays.
### 3. The Headless Service
We used a Headless Service (`clusterIP: None`) for our database. This gives our Spring Boot app a predictable internal DNS address: `postgres-0.postgres-service`.
### 4. The Secret
No passwords in plain text! We used a Kubernetes **Secret** to store our database credentials, injecting them into the Spring Boot container at runtime via environment variables.
### 5. Ingress
Router and reverse proxy that automatically discovers and configures routing for our services by connecting directly to Kubernetes.
---
## Deployment & Access
The stack is accessible via **NGINX Ingress**. The Ingress routes requests with the `/frontend-service` path to the internal `frontend-service` (`ClusterIP`) on port `80`.
```
http://<ingress-controller-address>/frontend-service
```
---
*GITHUB Repository & deployment files: [kubekanvas/deploy-springboot-kubernetes](https://github.com/kubekanvas/deploy-springboot-kubernetes.git)*
springbootingresspostgres+2 more
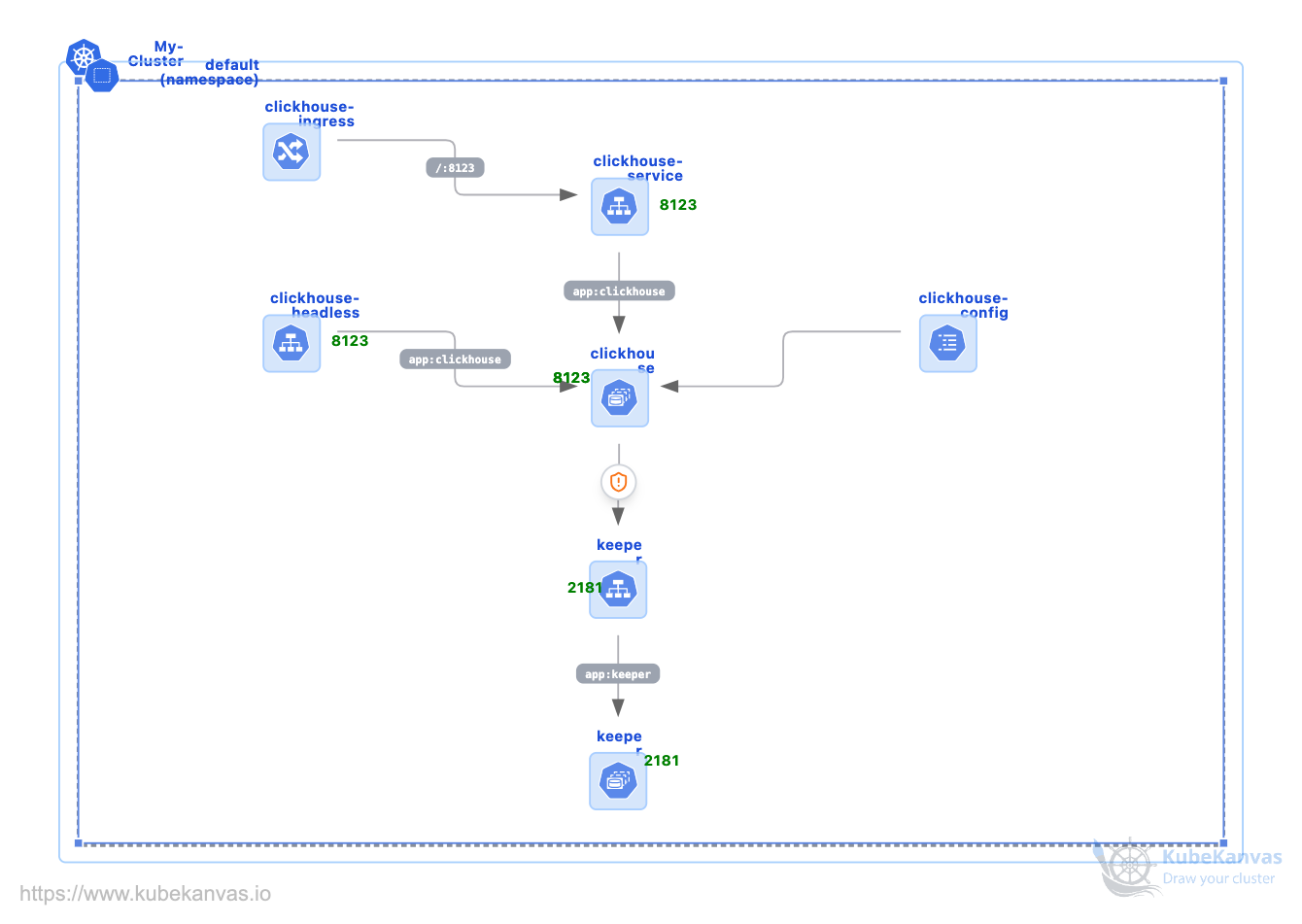
Deploying ClickHouse Through KubeKanvas Visual Editor
2 uses
## Deploying ClickHouse Via kubekanvas (a fast open-source column-oriented database management system that allows generating analytical data reports in real-time using SQL queries)
Follow these steps in order to replicate the environment or recover from a cluster reset.
1. **Install NGINX Ingress Controller:**
This command builds the "bridge" between your physical machine and the Kubernetes cluster.
`kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx/main/deploy/static/provider/cloud/deploy.yaml`
2. **Verify Ingress Controller Readiness:**
Wait until the status shows `Running`.
`kubectl get pods -n ingress-nginx`
3. **Watch the Startup Sequence:**
Monitor the pods until both `keeper-0` and `clickhouse-0` show `1/1 READY`.
`kubectl get pods -n clickhouse -w`
---
### Local Networking Configuration
Since you are using Docker Desktop, your computer needs to be told that `clickhouse.local` is actually your own machine.
4. **Update Windows Hosts File:**
* Open **Notepad** as Administrator.
* Open `C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts`.
* Append the following line and save:
`127.0.0.1 clickhouse.local`
---
### Data Verification (The Smoke Test)
With the network path established, we execute the first SQL commands via the Ingress.
5. **Create Schema and Insert Data:**
This command tests the **Write Path**: Ingress Service ClickHouse Pod Disk.
```bash
curl -X POST http://clickhouse.local --data-binary "
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS demo;
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS demo.events (id UInt32, message String) ENGINE = MergeTree() ORDER BY id;
INSERT INTO demo.events VALUES (1, 'clickhouse on kubernetes works');"
```
6. **Query the Data:**
This command tests the **Read Path** and verifies data persistence.
```bash
curl http://clickhouse.local --data-binary "SELECT * FROM demo.events;"
```
---
### Dashboard Access
7. **Open the Web UI:**
Navigate to `http://clickhouse.local/dashboard` in your browser.
* **User:** `default`
* **Password:** (Leave Blank)
---
## Summary of Components Created
| Command Target | Role |
| --- | --- |
| **Namespace** | Logical isolation for ClickHouse resources. |
| **ConfigMap** | Overrides `config.xml` (Cluster/Zookeeper) and `users.xml` (Auth). |
| **StatefulSet (Keeper)** | 1-node coordination engine for metadata. |
| **StatefulSet (Server)** | 1-node database engine with 10Gi Persistent Storage. |
| **Ingress** | Routes `clickhouse.local` traffic to the database service. |
kubernetesClickHousekubekanvas+1 more